Running POP and IMAP Daemons:
The test in The POP listing shows POP running, and the test in the IMAP listing shows imapd up and running. However, a test on a freshly installed Red Hat system returns the Connection refused error.
$ telnet localhost imap
Trying 127.0.0.1...
telnet: connect to address 127.0.0.1: Connection refused
$ telnet localhost pop3
Trying 127.0.0.1...
telnet: connect to address 127.0.0.1: Connection refused
Among the possible causes for this error on the localhost may be that you have not installed POP or IMAP. POP and IMAP can be installed during the initial installation, or installed later using RPM. If your system does not have POP and IMAP, the source code for a popular version of these daemons can be obtained via anonymous FTP from ftp.cac.washington.edu, where it is stored in the /imap/imap.tar.Z file. Our sample Red Hat system does have POP and IMAP installed, as the figure illustrates.
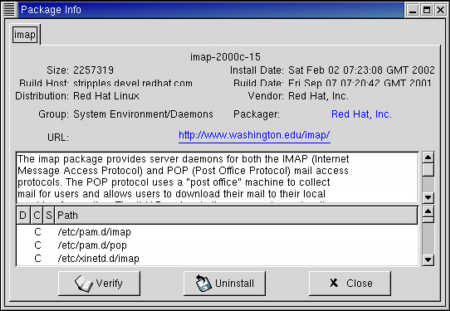
Both POP and IMAP are contained in the IMAP RPM. the previous figure shows the gnorpm query of the IMAP package on our sample Red Hat system. The query shows that IMAP is installed, and examining the details provided by the query would show that POP is included in the package. Yet, neither the IMAP daemon nor the POP daemon responds to connections. The Connection refused error appears even on our sample Red Hat system, on which the software was installed during the initial installation.
Red Hat starts both POP and IMAP from xinetd. The /etc/xinetd.d directory contains five different
xinetd configuration files relating to POP and IMAP:
- imap xinetd uses this file to start IMAP when traffic arrives on port 143.
- ipop2 xinetd uses this file to start POP2 when traffic arrives on port 109. POP2 is rarely used.
- ipop3 xinetd uses this file to start POP3 when traffic arrives on port 110. POP3 is the version of POP most often used.
- imaps xinetd uses this file to start IMAP version 4 when traffic arrives on port 993. Port 993 is used for IMAP traffic when that traffic is encapsulated in an SSL tunnel.
- pop3s xinetd uses this file to start POP3 when traffic arrives on port 995. Port 995 is used for POP traffic when that traffic is encapsulated in an SSL tunnel.